At the end of October I attended the CPATH 2017 (Canadian Professional Association for Transgender Health) conference in Vancouver. It was a fascinating event from which I learned a great deal. I’m keen to share some of my thoughts and experiences with others, as I feel there is a great deal that trans health researchers, practitioners and activists can learn from the progress that’s been made in Canada, as well as the limitations of that progress.
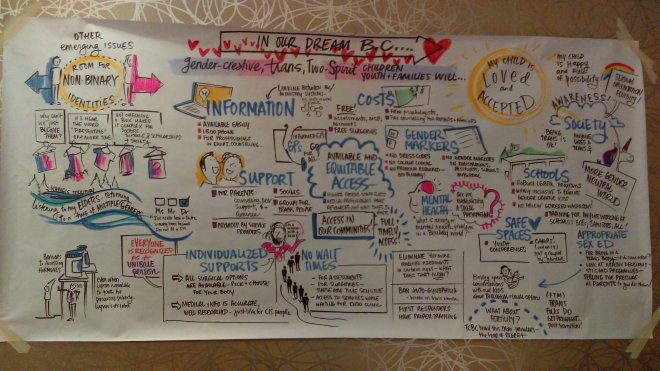
Poster: “In Our Dream B.C….”, by Drawing Change. Based on Trans Care BC consultation with gender creative, trans, and two-spirit youth and their families..
In this post, I reflect briefly on my impressions of the conference, and link to Twitter threads I wrote during various sessions. You can also read my initial thoughts on the conference here.
CPATH took a broadly holistic approach to trans health
Over 300 people took part in the three-day CPATH 2017 conference and two-day pre-conference. In attendance were GPs, nurses, endocrinologists, psychologists, psychiatrists, therapists and counsellors, social workers, healthcare administrators, peer and parent support group facilitators, academic researchers, lawyers, politicians, and various trans campaigners.
CPATH 2017 treated “health” as a social phenomenon as well as a purely embodied matter, and this made for some very productive conversations. For example, numerous sessions explored how trans healthcare might best be provided in the context of primary health. Gender identity services are frequently provided by GPs with support from external specialists, a model of care that is currently under consideration for England. In some Canadian Provinces, organisations such as Trans Care BC help to connect providers in primary care to relevant specialists, and support trans people in obtaining interventions such as hormone therapy and surgeries.
This approach enables continuity of care in a local context, with family doctors enabled to provide trans-specific care for their patients alongside everyday services. It reduces barriers to access such as waiting times and the necessity of long-distance travel. It also enables GPs to help their trans patients access a wider range of specialist services: for instance, trans people with mental health issues might benefit from a referral to a peer support group as well as or instead of formal therapy (depending on patient desire and need). Many practitioners provide services on the basis of informed consent, rather than using mental health assessments as gatekeeping measures. It was heartening to see generalist and specialist healthcare professionals, social workers, trans activists and others engaged in open discussions about how best to manage care through this kind of system.
I was also particularly struck (and moved) by a session entitled Trans and Two Spirit Youth Speak Back! The 40 or so adults in attendance – mostly healthcare professionals or researchers of one stripe or another – were asked not to speak at all during this workshop. We were instead invited to listen to the stories and experiences of trans and two-spirit young people, who sat dotted around the room and answered pre-prepared questions delivered by a youth group facilitator. This session structurally prioritised the voices of young trans people who are so often silenced, and also offered an opportunity for us to hear how the healthcare needs and challenges faced by these individuals were shaped by their cultural heritage, family life, schools and peer groups.
CPATH took intersectional trans voices seriously
Trans and Two Spirit Youth Speak Back! was just one example of how trans voices were frequently centred at CPATH 2017. As an attendee from the UK, I was very impressed by this! Our trans healthcare conferences, seminars and workshops tend to be organised by and for community groups, researchers or healthcare providers, with relatively little overlap between attendees at these events. Very few practitioners are (openly) trans, meaning that trans people tend to talk to one another at community and research events, but are heard less often at healthcare conferences for doctors, nurses and mental health specialists. Moreover, the speaker line-ups at all these events tend to overwhelmingly prioritise the most privileged individuals, such as white people and men. The only possible exception is cliniQ’s Trans Health Matters conference, and that event too feels like it’s taking the first steps towards something better.
During the opening plenary of the CPATH conference proper, we were informed that around one third of speakers at the event were trans, and around a tenth were Indigenous (i.e. of First Nations heritage). I’m not sure how many people of colour were represented at the event more generally, but the all-white panels which are a norm at UK events seemed few and far between.
Importantly, the trans women, trans men, non-binary and two-spirit platformed as speakers and workshop facilitators were usually also professionals. We weren’t simply present at CPATH to represent a “patient perspective”: rather, we were the experts. This reflects the hard work of individuals in pursuing a career, and the collective work of CPATH in supporting trans professionals; it also reflects the actions of local providers in various parts of Canada who have made an active effort to employ trans people, or secure funding for partnerships with trans-led organisations.
In my previous post I noted that the opening plenary of the conference proper centred Indigenous voices. This included a formal welcome from Musqueam Elder Jewel Thomas, and talks by trans and two-spirit Indigenous educators from different parts of North America. I was happy to see that the plenary session on the second day of the conference continued to centre the voices of individuals who tend to be marginalised within even trans spaces. Two-spirit physician Dr James Makokis and Latina trans activist Betty Iglesias – who discussed issues faced by trans sex workers and migrants – were platformed alongside an Member of Parliament from Canada’s ruling Liberal Party, resulting in a thoughtful and challenging debate.
CPATH (and the rest of us) still have a lot of work still to do
I left CPATH with a very positive impression, but Canada is by no means the promised land for trans health. Professionals and patient representatives alike frequently discussed the challenges they faced in providing gender-affirming services. Transphobia and cisgenderism are still very much prevalent within healthcare provision and legal frameworks, particularly outside of urban areas: there is therefore a great need for better education among trainees and further reform of laws and guidelines. Limited funding and different approaches across the country’s Provinces and Territories also mean that not everyone has the same access to treatment, and waiting lists persist for publicly-funded care. These are challenges that exist across the world, and may benefit from greater international collaboration and strategy-sharing.
At the end of the first day of the conference proper, there was a reception specifically for trans people attending the conference. I later reflected on the experience of attending this reception in conversation with a genderqueer colleague; both of us felt ourselves relaxing enormously upon entering the trans-only space. For all the positives of CPATH, it was a huge relief to step away from cisgenderist expectations and microaggressions that quietly persisted throughout the conference proper. These included a range of unspoken ideas about how we should dress, act, and talk “professionally”, limitations on our ability to name transphobia within healthcare settings without fearing repercussions, and the occasional terrible intervention from self-righteous cis professionals.
As ever, facing down these challenges is hardest for the most marginalised trans people, including (for instance) disabled individuals, sex workers, migrants, and people of colour. I was aware that while CPATH 2017 took a broadly intersectional approach, instances of ableism, racism, sexism and so on persisted: and this could take the form of unexamined prejudices on the part of more privileged trans people too. Moreover, white people were still heavily overrepresented among conference attendees; a phenomenon that was particularly noticeable at an event held in a city as diverse as Vancouver.
What I’m taking from this is a reminder that equality work is never “done”; rather, it is something that we should strive to always “do”. We should aim constant improvement in our relations to one another rather than assuming that solidarity and equality are things that we can simply achieve. It is in this spirit that I’ve attempted to use my own privilege as an academic to bring back lessons from Canada for the UK and beyond.
So, I’ll end this post with a serious of links to Twitter threads from the event. I livetweeted extensively from CPATH 2017, sharing summaries of the numerous talks and workshops I attended. This is by no means a comprehensive summary of any of the sessions I was at, let alone the wider conference (as numerous parallel sessions took place simultaneously). However, I hope the ideas and approaches will be as useful and interesting to you as they are to me.
Pre-conference (training) Twitter threads
Day 1:
Introduction to Gender-Affirming Practice
Pre-puberty/Puberty: Addressing On-coming Puberty
Day 2:
Adolescence: Moving Forward With Gender-affirming Care for Youth
Cross Country Health Clinic Practice Panel: Models of Care and Clinical Practices
Conference Twitter threads
Day 1:
Plenary: Centering Indigeneity and Decolonizing Gender
Interpersonal Communication Needs of Transgender People
Ethical Guidelines for Research Involving Trans People: Launch of a New Resource
Investigating the Medicalization of Trans Identity
Primary Care Approaches to Caring for Trans Youth
Day 2:
Plenary: Fostering Safety and Inclusion in Service Provision, Systems and Sectors
Non-binary Inclusion in Systems of Care
Trans Data Collection and Privacy
Legal, Ethical, Clinical Challenges: Youth Consent to Gender Affirming Medical Care
Day 3:
Plenary: Supporting Older Trans People






